Open on Evenings & Holidays! Extended And Flexible Hours!
* DNA Testing for Immigration
* Paternity Testing
* Deceased Paternity
* Forensic Testing & Much More!
Open on Evenings & Holidays! Extended And Flexible Hours!
* DNA Testing for Immigration
* Paternity Testing
* Deceased Paternity
* Forensic Testing & Much More!

AB DNA Testing Services
Phone: 718-701-0292
We offer New York’s BEST AND MOST AFFORDABLE DNA TESTING with a full range of services to verify family relationships.
We specialize in the following types of DNA tests:
• Paternity • Maternity • Grand-parenting • Sibling Relationship • Biological Relationship Studies • Twin Studies • Deceased Paternity • Forensic Testing • Child Identity Testing • Family Tree and Genealogy Testing
* EVEN LOWER PRICE THAN HOME DNA KITS.
* NO HIDDEN COSTS – Collection kits, photography, and fingerprinting all included.
* 99.9% (OR GREATER) ACCURACY.
* FINAL RESULTS ARE PRESENTED IN A NOTARIZED DOCUMENT IN A CLEAR AND CONCISE FORM.
* ALL RESULTS ARE COURT ADMISSIBLE.
* OVER 15 YEARS EXPERIENCE.
* NO REFERRALS NECESSARY!
* FAST AND PAINLESS SAMPLE COLLECTIONS, USING BUCCAL (Mouth) SWABS.
* SPANISH, PORTUGUESE, FRENCH AND CREOLE SPOKEN.
* PLEASE SEE TRANSLATIONS OF OUR SERVICES IN: SPANISH, BENGALI, URDU, CHINESE AND NEPALESE!
Located In Woodside Queens, easily reachable from all boroughs (Queens, Manhattan, Brooklyn, Bronx and Staten Island), Westchester, Nassau and Suffolk.
We can also schedule DNA tests at our network of collection sites throughout New York city.
Call us. We have found that in many cases, our personalized service can overturn your denial. We will call the passport office or immigration dept. for you and plead your case over phone verbally.
90% of time they will revoke your denial, as long as you get the required information to them quickly.
AB DNA TESTING SERVICES
AB DNA Testing Services © |
 |
718-701-0292 We are open on evenings & holidays! |
 |
Legal Paternity Test: $349
NYS compliant testing only. NO HIDDEN COSTS OR EXTRA FEES.
We do not provide prenatal DNA testing in-house. If you need prenatal testing, we can refer you to a provider we’ve worked with previously:
Prenatal DNA Testing NYC.
AB DNA Testing Services offers a broad range of DNA testing options using certified, accredited laboratories and verified collection procedures.
Our DNA is more than just a biological blueprint — it’s a living record of our ancestral history. Through family tree and genealogy DNA testing, people are discovering where they come from, uncovering long-lost relatives, and filling in missing branches of their family trees. Whether you’re beginning your ancestry journey or seeking to complete your genealogy research, DNA testing is one of the most powerful tools available today.
In this guide, we’ll explore how genealogy testing works, what you can learn from it, and why it’s becoming a popular choice for families in Queens and across the world.

Genealogy DNA testing is a type of genetic analysis that reveals your ethnic origins and familial connections. It looks at markers within your DNA that are passed down from generation to generation. There are three primary types of DNA used for genealogy testing:
Genealogy DNA testing allows you to build your family tree, verify relationships, and discover ancestral roots that might not be recorded in any paper trail.
Genealogy DNA tests provide an ethnic breakdown of your ancestry, often divided into percentages by geographic regions. This can uncover connections to:
Many ancestry DNA services include access to a matching database where you can find genetic relatives — including cousins, siblings, and even parents you may not know. These connections can open the door to powerful family reunions and life-changing stories.
DNA testing helps confirm the accuracy of your family tree by supporting or disproving relationships. It’s especially useful in cases where adoption, unknown parentage, or family secrets may have left gaps or inconsistencies.
By documenting your ancestry through DNA, you create a legacy for future generations. Your children and grandchildren will have a clearer understanding of their roots, culture, and identity.
While genealogy testing is primarily for ancestral discovery, some services also offer health reports based on your genetics. This can give insight into inherited traits and potential health risks, bridging the gap between your family’s past and your health future.
Genealogy DNA testing is simple, convenient, and completely non-invasive. Here’s how it works:
As with any DNA testing, privacy is a valid concern. When choosing a genealogy testing provider, make sure they offer:
At AB DNA Testing Services, we take your privacy seriously and ensure that your results are handled with full confidentiality and transparency.
When it comes to family tree and genealogy DNA testing, not all services are created equal. Look for a provider that offers:
At AB DNA Testing Services, we offer reliable, scientifically backed DNA testing that helps you uncover your roots and connect with your heritage. Whether you’re just starting your genealogy journey or adding to a well-researched family tree, we’re here to help you make sense of your past — and preserve it for future generations.
Explore your heritage with confidence and clarity. Call or visit us today to learn more about our genealogy and ancestry testing services.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
Phone: 718-701-0292
Let us help you uncover the roots of your family tree. Your story is in your DNA — and it’s waiting to be discovered.
Can DNA testing confirm if someone is your sibling or grandparent? Establishing family relationships can sometimes be a complex journey, especially when direct parental DNA is unavailable. In these situations, sibling and grandparent DNA testing becomes a powerful alternative. These tests help determine biological connections by analyzing shared genetic markers — often serving as the key to unlocking answers in legal, personal, or immigration matters.
If you’re in a situation where you need to confirm siblinghood or grandparent relationships, understanding how these DNA tests work and when they’re needed is essential. In this guide, we explore what these tests are, how accurate they can be, and why choosing an experienced DNA testing provider matters.

Sibling DNA testing is used to determine whether two or more individuals share one or both biological parents. There are two primary types of sibling testing:
This type of test is often requested in cases where the alleged parent is deceased, unavailable, or unwilling to participate in testing.
Grandparent DNA testing is designed to determine whether an individual is biologically related to one or both grandparents. It is commonly used when a parent is not available for testing, allowing the grandparent(s) to serve as a proxy for establishing a familial link.
There are two variations:
In legal situations, such as custody or inheritance disputes, this testing may provide critical evidence in determining family relationships.
These tests can be used in a variety of personal and legal contexts:
The testing process for siblings and grandparents is straightforward and non-invasive:
While sibling and grandparent DNA tests are highly useful, they rely on statistical probability rather than definitive match/no-match results like parentage tests. Accuracy can vary depending on:
That’s why it’s important to work with a laboratory that can advise you on the most accurate testing strategy for your specific case.

Like other DNA tests, sibling and grandparent DNA testing is available in two formats:
At AB DNA Testing Services, we specialize in accurate and compassionate DNA testing for complex family relationships. Whether you need a test for legal, immigration, or personal purposes, we provide:
Have questions about whether sibling or grandparent DNA testing is right for your situation? We’re here to help.
AB DNA Testing Services
718-701-0292
Call today to schedule a consultation. Our experienced team is ready to help you confirm the family connections that matter most — accurately, confidentially, and professionally.
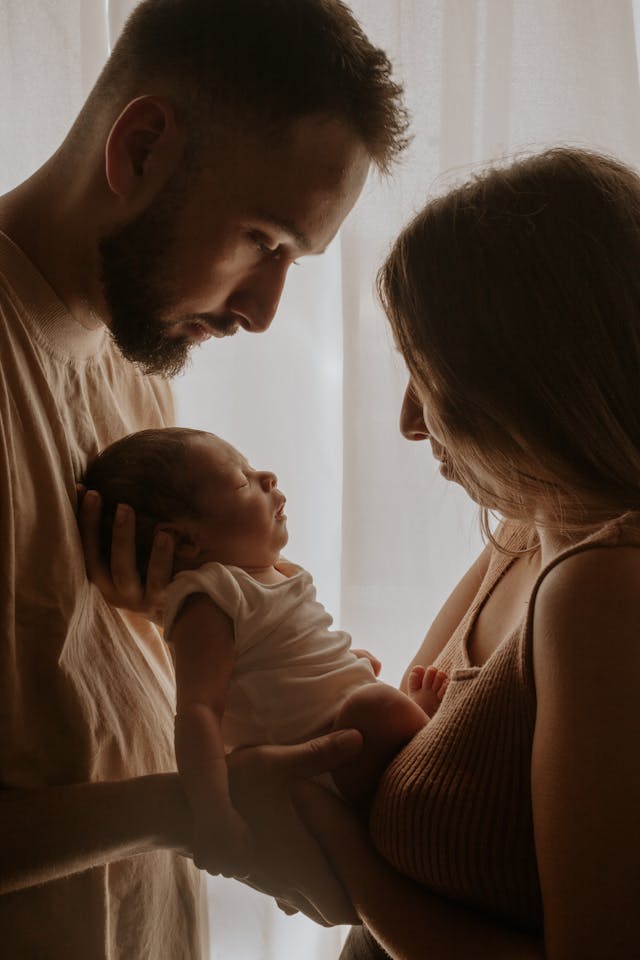 When and why is paternity and maternity DNA testing important? DNA testing has become a reliable and essential resource for confirming biological relationships. Whether it’s for legal clarity, immigration requirements, or personal peace of mind, paternity and maternity DNA testing provides scientific answers to questions that once required years of uncertainty or guesswork. These tests play a vital role in a wide range of situations, from establishing parental rights to resolving inheritance disputes. In this article, we’ll explore why these tests are important, how they work, and how to ensure you’re getting accurate and legally recognized results.
When and why is paternity and maternity DNA testing important? DNA testing has become a reliable and essential resource for confirming biological relationships. Whether it’s for legal clarity, immigration requirements, or personal peace of mind, paternity and maternity DNA testing provides scientific answers to questions that once required years of uncertainty or guesswork. These tests play a vital role in a wide range of situations, from establishing parental rights to resolving inheritance disputes. In this article, we’ll explore why these tests are important, how they work, and how to ensure you’re getting accurate and legally recognized results.
Paternity DNA testing determines whether a man is the biological father of a child, while maternity DNA testing confirms a woman’s biological relationship with a child. Both tests use a simple and non-invasive sample collection — typically a cheek swab — from the individuals being tested. The collected DNA is analyzed and compared to determine if there is a genetic match.
These tests serve a range of personal, legal, and medical purposes. Here are some of the key reasons people choose to have a paternity or maternity test:
In immigration cases, proving a biological relationship between a U.S. citizen or permanent resident and a foreign-born child or parent may be required. U.S. embassies and USCIS accept only DNA test results from accredited laboratories for legal immigration applications.
In cases of adoption, maternity or paternity testing may be used to confirm biological relationships. It’s also helpful in family reunification efforts when long-lost or separated family members want to confirm kinship.
Sometimes, individuals seek paternity or maternity testing for personal reasons — to remove doubt, bring closure, or build emotional bonds with family members. Knowing the truth can foster stronger family connections and reduce emotional stress.
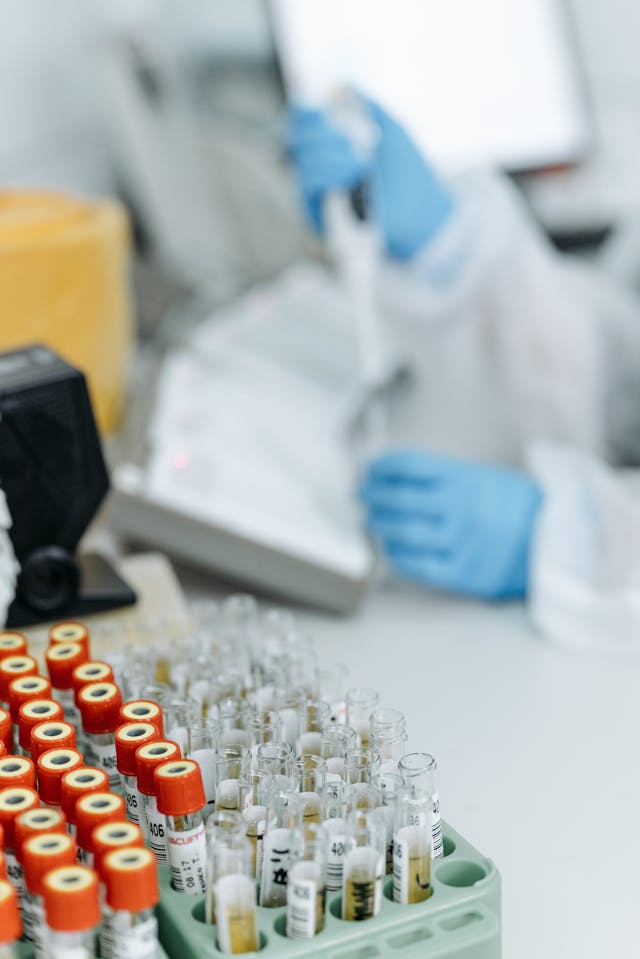 DNA testing for paternity or maternity is simple and stress-free:
DNA testing for paternity or maternity is simple and stress-free:
It’s important to distinguish between legal DNA testing and peace-of-mind testing:
Accuracy, reliability, and confidentiality matter when choosing a DNA testing service. Be sure to choose a provider that is:
At AB DNA Testing Services in Queens, we provide fast, confidential, and court-admissible paternity and maternity testing for families, legal cases, and immigration purposes. Our experienced staff ensures the process is easy, supportive, and secure from start to finish.
Whether you need answers for legal, personal, or immigration reasons, AB DNA Testing Services is here to help you uncover the truth with confidence and care.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
Phone: 718-701-0292
Call now to schedule your consultation. We’re here to provide clarity, comfort, and certified DNA testing you can trust.
In this post, we’ll explore how DNA testing supports immigration-related legal cases, what the process involves, and why it’s vital to choose the right provider. In today’s global world, families often span continents. For those navigating the complex legal landscape of immigration, DNA testing has become an essential and reliable method to verify biological relationships. Whether it’s for family reunification, visa applications, or citizenship petitions, immigration DNA testing plays a crucial role in ensuring legal processes move forward smoothly and truthfully.

Immigration DNA testing is a scientific method used to confirm familial relationships when required by immigration authorities. In cases where birth certificates or other documentation are missing, insufficient, or disputed, a DNA test can provide definitive proof of a biological relationship — such as parent-child, sibling, or grandparent-grandchild.
This type of testing is often required by:
In family-based immigration cases, the U.S. government requires proof of a biological relationship between a petitioner (usually a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident) and a beneficiary (the family member seeking entry). If documents alone are insufficient, DNA testing becomes the most accepted and definitive method to establish that relationship.
In cases where immigration petitions are denied due to lack of evidence, DNA testing can serve as the critical piece of evidence that reverses a decision. Many legal teams rely on certified DNA test results when preparing appeals or presenting additional evidence to immigration courts.
For refugees and individuals seeking asylum who have been separated from their families due to war, displacement, or crisis, DNA testing may be the only way to prove familial ties — often making the difference between being reunited or remaining apart.
Getting a DNA test for immigration purposes is straightforward when handled by a qualified provider. Here’s how the process typically works:
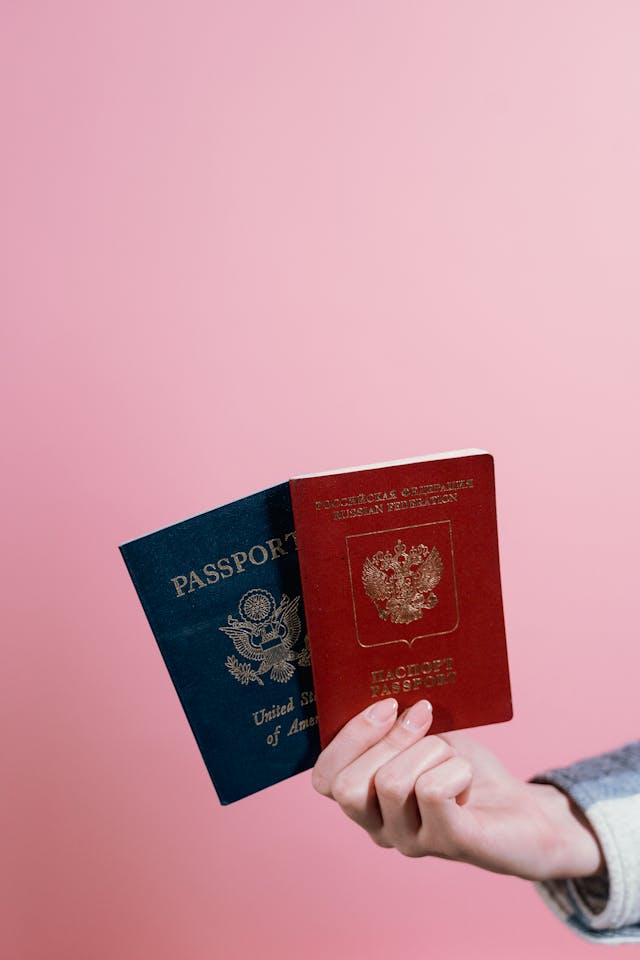 Immigration isn’t the only area where DNA testing proves invaluable. At AB DNA Testing Services, we also provide accurate, court-admissible testing for:
Immigration isn’t the only area where DNA testing proves invaluable. At AB DNA Testing Services, we also provide accurate, court-admissible testing for:
With sensitive personal information at stake, privacy is a top priority. Always choose a DNA testing provider that offers:
At AB DNA Testing Services, we adhere to the highest standards of data protection and only share your results with the required legal parties.
When selecting a provider for immigration DNA testing, look for:
At AB DNA Testing Services ®, we specialize in immigration DNA testing that meets all USCIS, embassy, and consular requirements. Our expert team ensures your sample is collected professionally, handled securely, and delivered with precision.
Whether you’re sponsoring a child, parent, or sibling for a U.S. visa — or responding to a government request for evidence — we’re here to help you navigate the process with confidence and ease.
AB DNA Testing Services ®
718-701-0292
Call now to speak with an immigration DNA specialist and schedule your appointment. Let us help you bring your family together — legally, securely, and with peace of mind.
Looking to learn more about the safety and accuracy of prenatal DNA testing? DNA testing has revolutionized how we understand biological relationships, medical conditions, and even our family histories. Among its many applications, prenatal DNA testing stands out for its ability to provide expectant parents with vital information before a child is even born. But how safe and accurate is it? This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about prenatal DNA testing — how it works, what it reveals, and why it’s one of the most trusted tools in modern genetics.
Prenatal DNA testing refers to a variety of genetic tests that can be performed during pregnancy to gather information about the fetus. The most commonly performed prenatal DNA test is Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), which analyzes small fragments of fetal DNA that are present in the mother’s bloodstream. This method can determine paternity, detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, and reveal the baby’s sex — all without putting the mother or baby at risk.
Safety is a primary concern for expectant parents considering genetic testing. Fortunately, non-invasive prenatal DNA tests are considered extremely safe. These tests only require a simple blood draw from the mother and a cheek swab from the potential father if paternity is being tested. Unlike traditional procedures like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), NIPT does not carry the risk of miscarriage because it does not involve inserting needles into the uterus.
Modern prenatal DNA tests are highly accurate. When performed by an accredited laboratory:
It’s important to note that while NIPT is extremely accurate, it’s still considered a screening test — diagnostic tests may still be recommended depending on the results.
Non-invasive prenatal DNA testing can typically be performed as early as 8 to 10 weeks into the pregnancy. The early availability of these tests makes them especially useful for expecting parents who want to be proactive about planning for their child’s health and well-being.
While prenatal DNA testing is essential for expecting families, DNA testing serves many other purposes:
Your choice of provider can make all the difference in the quality and reliability of your results. Look for a testing center that is:
Understanding your genetic information can be empowering, especially during pregnancy. Prenatal DNA testing not only provides answers but also offers peace of mind. Whether you’re confirming paternity, screening for genetic conditions, or simply looking for early insights into your baby’s development, a reputable DNA testing service can be a valuable partner in your prenatal journey.
AB DNA Testing Services ® is proud to provide fast, accurate, and confidential prenatal DNA testing in Queens, NY. We also specialize in immigration, paternity, and legal DNA testing. If you’re expecting a child and want reliable, non-invasive testing you can trust, we’re here for you.
AB DNA Testing Services
718-701-0292
Call today to speak with a DNA testing specialist and schedule your appointment. Your peace of mind is just one test away.
This blog explores what to expect during a dna test appointment and provides insights into how it works and its significance. DNA testing has become an indispensable tool in resolving questions related to relationships, ancestry, and legal matters. From confirming paternity to supporting immigration cases, DNA testing offers accurate and reliable results.

DNA testing has applications ranging from personal identification to legal cases. It helps confirm biological relationships, supports legal disputes, and uncovers family history. These tests are conducted with high accuracy, ensuring you get the answers you need with confidence.
Preventive measures can ensure the security of your genetic data and its ethical use. Choose certified testing facilities with stringent data protection policies. Verify how your sample and results will be handled to ensure confidentiality.
Before choosing a DNA testing provider, evaluate the laboratory’s certifications, the range of services offered, and their expertise. Consider whether the provider can accommodate your specific needs, such as legal, medical, or genealogical testing.
Need reliable DNA testing services? Contact AB DNA Testing Services © today to schedule your appointment.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
Phone: 718-701-0292
Do you have questions about DNA testing for paternity? Let’s dive into this topic. Determining paternity can be an essential step for various reasons, including legal matters, child support, inheritance, and personal peace of mind.
DNA testing is the most reliable and accurate method for establishing paternity. In this blog, we’ll discuss the importance of paternity testing, the different types of tests available, the process involved, and how to interpret the results.

Paternity testing can have significant implications for both the child and the parents. Here are some reasons why establishing paternity is important:
There are several types of paternity tests, each designed for different situations and levels of accuracy.
A home DNA paternity test is a convenient and private option for individuals who want to determine paternity without legal involvement.
A legal DNA paternity test is required for situations where the results need to be legally admissible, such as in child support cases, custody disputes, and immigration matters.
The process of DNA paternity testing involves several key steps to ensure accuracy and reliability.

Understanding the results of a paternity test is crucial for making informed decisions.
DNA paternity testing is the most reliable method for determining biological fatherhood, offering clarity and resolution for various personal, legal, and medical situations. By understanding the different types of paternity tests, the testing process, and how to interpret the results, you can make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to address your specific needs.
For professional and accurate DNA paternity testing services, contact AB DNA Testing Services in Queens NY today!
AB DNA Testing Services ©
718-701-0292
 What type of prenatal DNA testing is best for your situation? Prenatal DNA testing has become an essential tool for expectant parents, providing valuable information about the health and development of their unborn child. With several types of prenatal DNA tests available, it can be challenging to determine which one is right for you. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of prenatal DNA testing, their benefits, and considerations to help you make an informed decision.
What type of prenatal DNA testing is best for your situation? Prenatal DNA testing has become an essential tool for expectant parents, providing valuable information about the health and development of their unborn child. With several types of prenatal DNA tests available, it can be challenging to determine which one is right for you. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of prenatal DNA testing, their benefits, and considerations to help you make an informed decision.
There are several types of prenatal DNA tests, each with specific purposes and benefits. The main types include Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS), and Amniocentesis.
NIPT is a non-invasive test that analyzes small fragments of fetal DNA circulating in the mother’s blood. This test can be performed as early as the 10th week of pregnancy.
Safety: NIPT poses no risk to the fetus, as it only requires a blood sample from the mother.
CVS is an invasive test that involves taking a small sample of cells from the placenta, typically performed between the 10th and 13th weeks of pregnancy.
Amniocentesis is another invasive test that involves extracting a small amount of amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus. It is usually performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy.
Selecting the appropriate prenatal DNA test depends on several factors, including your medical history, risk factors, and personal preferences. Here are some key considerations to help you decide:

Discussing your options with your healthcare provider is essential for making an informed decision. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your medical history, risk factors, and preferences.
Choosing the right prenatal DNA test is a crucial decision that can provide valuable insights into your unborn child’s health and development. By understanding the different types of DNA tests, their benefits, and considerations, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your needs and preferences.
For professional and reliable prenatal DNA testing services, contact AB DNA Testing Services today for a consultation.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
718-701-0292
How you choose the right DNA testing service is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable results, whether you’re testing for ancestry, health insights, or legal purposes. With many options available, it can be challenging to determine which service best suits your needs. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the key factors to consider when selecting a DNA testing service.

The first step in choosing a DNA testing service is to identify your specific needs. Different tests are designed for different purposes, so it’s important to understand what you want to achieve with your DNA test.
Ensure that the DNA testing service uses a laboratory that is accredited by recognized organizations. Accreditation ensures that the laboratory meets high standards for accuracy and reliability.
Different DNA testing services offer a variety of tests and additional features. Consider what services and features are important to you.
The cost of DNA testing services can vary widely. It’s important to compare prices and understand what is included in the cost.
Your genetic data is highly personal, so it’s essential to choose a DNA testing service that prioritizes privacy and security.
Customer reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the reliability and quality of a DNA testing service.

Knowing what to expect from the testing process and how long it will take to get your results is important.
Choosing the right DNA testing service involves considering your specific needs, the accreditation of the laboratory, the range of services offered, cost, privacy policies, reviews, and the process involved. By taking these factors into account, you can select a service that provides accurate, reliable, and secure DNA testing.
For professional DNA testing services in New York City and the Tri-State area, contact AB DNA Testing Services in Queens NY.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
718-701-0292
What does the future of DNA testing hold? DNA testing has transformed various fields, from healthcare and forensics to ancestry and genealogy. As technology continues to advance, the future of DNA testing promises even more remarkable developments and applications. In this blog, we’ll explore the exciting trends and innovations shaping the future of DNA testing, and how they will impact our lives.

One of the most significant trends in DNA testing is the continuous improvement of DNA sequencing technologies. These advancements are making DNA testing faster, more accurate, and more affordable.
The integration of DNA testing into healthcare is paving the way for personalized medicine, where treatments and preventive strategies are tailored to an individual’s genetic profile.
DNA testing has already revolutionized forensic science, and future advancements promise to enhance its capabilities further.

The future of DNA testing includes the integration with digital health platforms, providing individuals with easy access to their genetic information and personalized health recommendations.
As DNA testing technology advances, it is essential to address the ethical and legal considerations associated with its use.
The future of DNA testing holds immense promise, with advancements in technology driving new applications and improving existing ones. From personalized medicine and enhanced forensic capabilities to the integration with digital health platforms, DNA testing is set to play an increasingly significant role in our lives. As we embrace these innovations, it is essential to address the ethical and legal considerations to ensure that DNA testing is used responsibly and for the benefit of all.
For cutting-edge DNA testing services and expert guidance, contact AB DNA Testing Services.
AB DNA Testing Services ©
718-701-0292